-

Land-to-sea spatial management
Research ProjectAssessing sediment effects on seafloor primary production via satellite . -

New study reveals colossal scale of riverbank erosion during Cyclone Gabrielle
Media release25 August 2025Over 220,000 m3 of sediment was eroded from just 9.1km of Ūawa/Hikuwai riverbanks in Gisborne (Tairāwhiti). -

Staff Profile Clare Wilkinson
Publication article24 February 2025Introducing NIWA sediment transport scientist Clare Wilkinson. -

Impacts of sediment on freshwater and estuarine and freshwater fish species
These fact sheets bring together existing scientific information on these effects, along with expert scientific knowledge, in an easy-to-read format by community groups and land-water managers interested in protecting mahinga kai. -
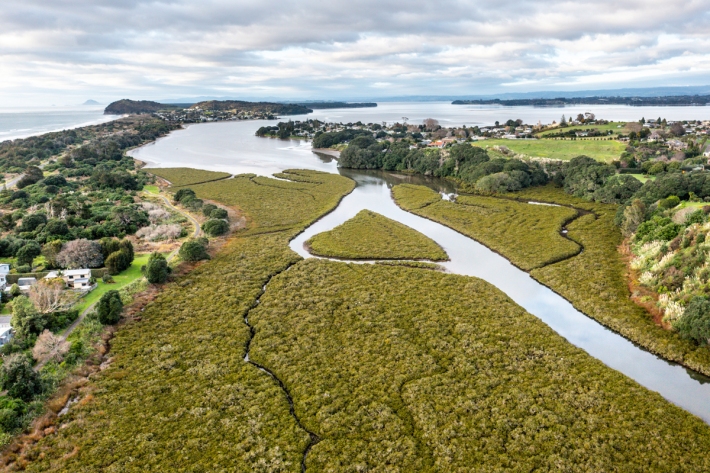

Understanding the threat of sea level rise to NZ’s wetlands
Media release07 October 2022Specialised monitoring equipment has been installed in Bay of Plenty estuaries to understand whether our coastal wetlands can survive the threat of inevitable sea-level rise. -

Survey provides snapshot of harbour’s health
News article10 May 2022Greater Wellington Regional Council regularly assess sediment quality and seafloor community health in the subtidal areas of Te Awarua-o-Porirua (Porirua Harbour) and Te Whanganui-a-Tara (Wellington Harbour). -

Microplastics: a deeper problem than we thought?
There is increasing global concern about the presence of plastic pollution in our oceans. -
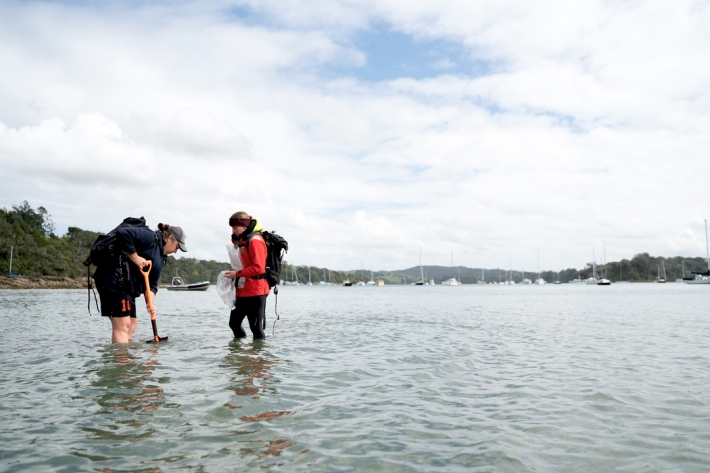

Keeping tabs on muddy waters
Feature story11 February 2021Sam Fraser-Baxter heads out with a NIWA research team keeping a close eye on these vulnerable transition zones. -

Norse goddess reveals seabed secrets
Feature story11 February 2021A large, orange Scandinavian robot gives NIWA’s marine geologists an in-depth look at changes to the seafloor off Kaikōura. -
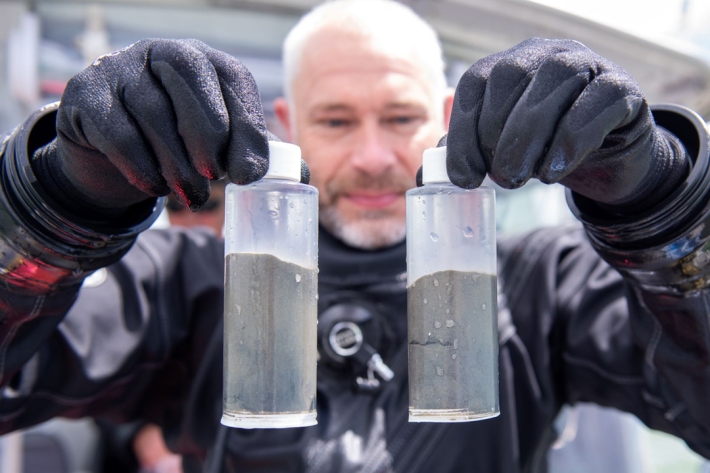

NIWA science divers finish mud marathon
Feature story04 January 2021Where there’s mud, there’s scientists. NIWA divers recently got down and dirty while completing a harbour-wide dive survey in the Wellington area. -
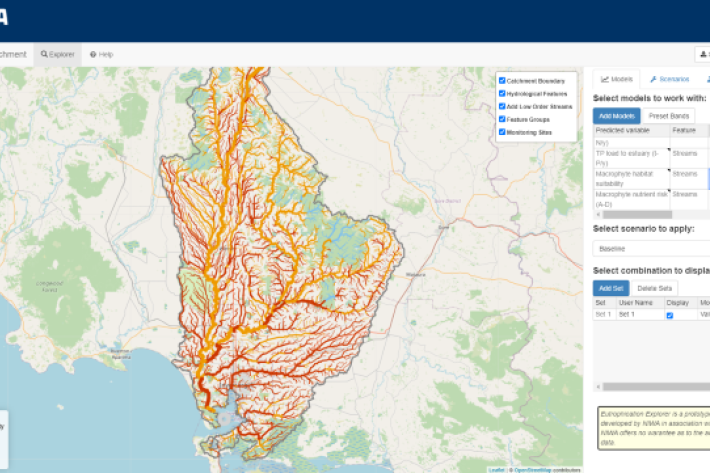
Eutrophication Explorer
A web application tool to explore monitoring data and model predictions related to stream and estuary eutrophication -
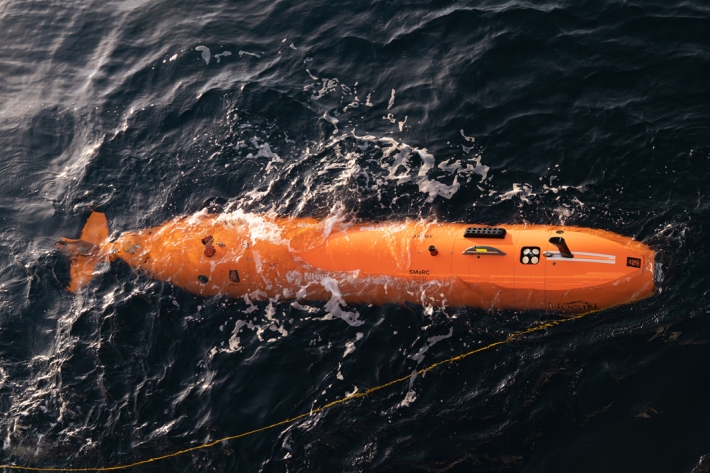

Underwater robot getting close-up look at Kaikōura Canyon
Media release08 October 2020A six-metre long orange underwater robot is flying through the Kaikōura Canyon for the next month collecting information on how the canyon has changed since the 2016 earthquake.
