-

Tuna - freshwater eels in New Zealand
Tuna is a generic Māori word for freshwater eels. The word will be used interchangeably in this resource. -

Lake Ōmāpere and the Utakura River
Tuna harvested from Lake Ōmāpere and Utakura River catchment have long comprised an important fishery for tangata whenua. -

Tuna - identification
There are several ways to tell the three New Zealand eel species apart. -

Estuary origins
In comparison to the vast span of geological time, the estuaries that we see today are very recent coastal features. -

Tuna - life cycle and leptocephalii
Freshwater eels have an unusual life cycle which sees them travelling between the ocean, estuaries and freshwaters. -
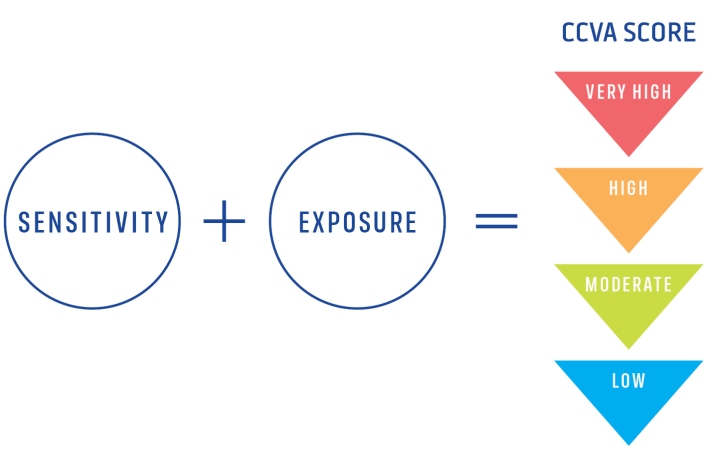
Climate Change Vulnerability Assessment (CCVA)
ServiceTo prepare for changes in climate, our freshwater and oceans decision-makers need information on species vulnerability to climate change. -

Tuna - habitat
Tuna are found in all sorts of habitats (places), including coastal estuaries, lakes, wetlands, rivers, mountain streams and even alpine tarns. -
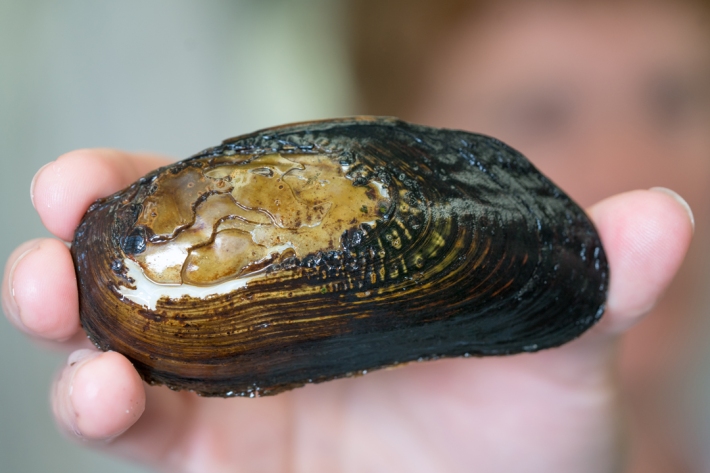

Taonga Species Series: Kākahi
Feature story06 June 2017What does science tell us about New Zealand freshwater mussels? -

Tuna - diet
Longfin eels are the largest and longest-lived fish in New Zealand's freshwaters, and where they are present they are the top predator. -
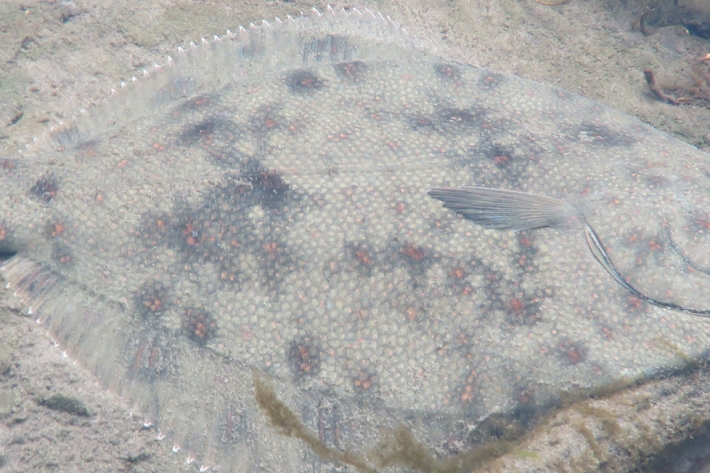

Taonga Species Series: Pātiki
Feature story06 June 2017What does science tell us about New Zealand flounder? -

Tuna - maturation and identifying sex
The sex of tuna is not determined genetically, as in some other organisms. -

Tuna - age and methods of ageing
Knowing the age (i.e. proportion of young vs. old) of eels in an eel population provides an understanding of how fast they grow and may give an indication of the pressures faced by tuna in a particular environment or habitat.
