Technical information about our datasets and methodology along with related resources.
Source information - NZ region bathymetry (2016)
Published by the National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Ltd.
Copyright © All rights reserved
All data used in the compilation is held at the National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA). Bathymetry is compiled from multibeam and single-beam data sourced from surveys by NIWA and Land Information New Zealand (LINZ), as well as international surveys by vessels from United States of America, France, Germany, Australia and Japan. In addition, scientific community data is sourced from the National Geophysical Data Centre (United States) and General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO_08 Grid, version 20120927).
Onshore representation derived from Land Information New Zealand topographic and the Ministry for the Environment LCDB II digital datasets.
Map information and metadata
Offshore representation was generated from digital bathymetry at a grid resolution of 250m. Sun illumination is from an azimuth of 315° and 45° above the horizon.
Projection Mercator (WGS84 datum).
Scale 1:5,000,000 at 41°S.
Not to be used for navigational purposes
Bibliographic reference
Mitchell, J.S., Mackay, K.A., Neil, H.L., Mackay, E.J., Pallentin, A., Notman P., 2012. Undersea New Zealand, 1:5,000,000.
NIWA Chart, Miscellaneous Series No. 92
Source information - NZ region bathymetry (2008)
Bathymetric compilation, interpretation, and terrain model by Charting Around New Zealand (CANZ) group.
Bathymetry compiled from data held at the National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research (NIWA); Hydrographic Office, Royal New Zealand Navy; National Geophysical Data Centre (U.S.); South Pacific Applied Geoscience Commission (Fiji); published scientific papers; recent swath bathymetric surveys funded by NIWA, Institute Francais de Recherche pour l’Exploitation de la Mer (IFREMER), France; Seabed Mapping New Zealand Limited and Land Information New Zealand (LINZ).
Onshore data are derived from Eagle Technology Ltd.’s EagledataTM, which is a derivative of the 1:50 000 Digital Vector Topographic Land Information New Zealand dataset.
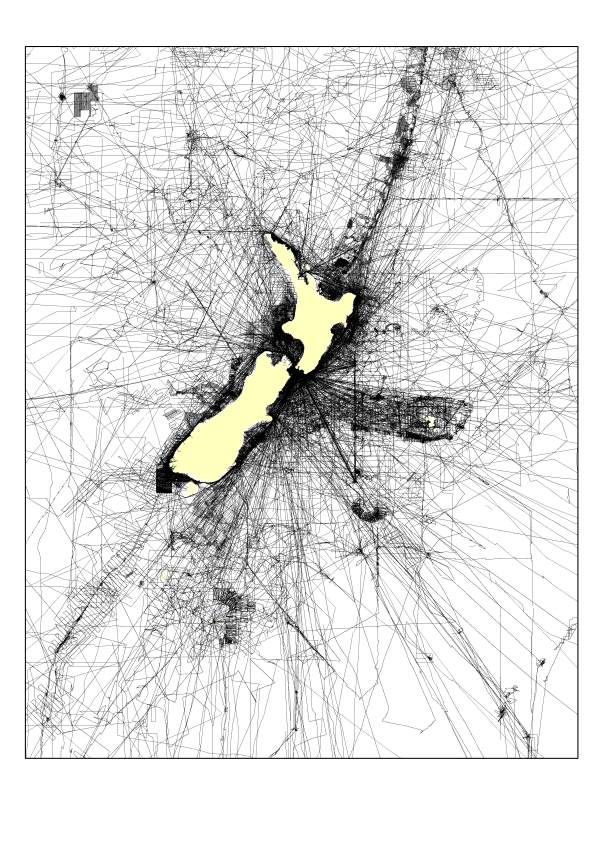
Ships’ tracks
5,005,568 km of single beam ship tracks providing depth information. Data confidence is greater in areas of dense coverage (black) versus areas of sparse to no coverage (white). See Figure 1. to the right.
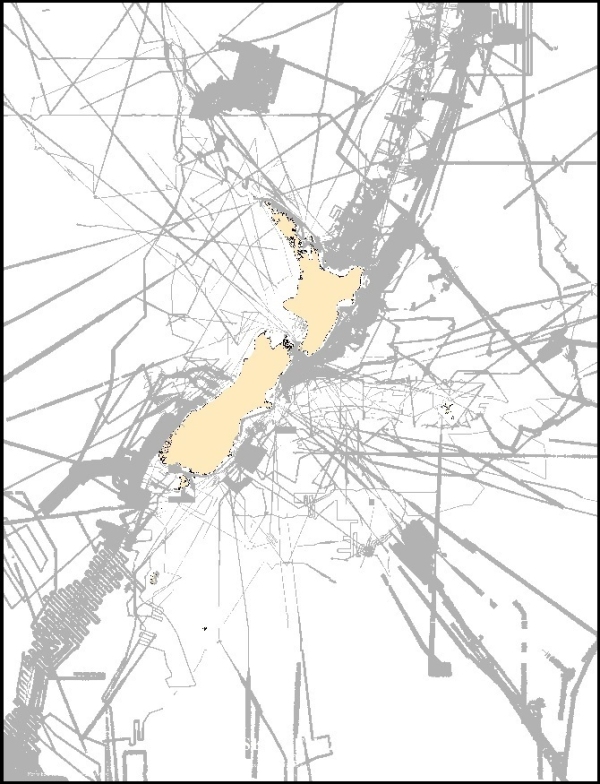
Multibeam swath locality diagram
Areas (2,593,115 km2, including overlaps) where multibeam swath depth information of the seafloor around New Zealand have been acquired. The resulting surveys show far greater detail than multiple lines using a single beam echo sounder. See Figure 2.
Bathymetric tints
These are the colour coded depths on our bathymetry charts. See Figure 3. and 4.

How do we map the sea floor?
The sea floor is mapped using various types of echo sounders. Single beam echo sounders, which direct a single beam of sound to the seabed directly below a ship, only provide depth information along the ship's trackline. Tracklines are often spaced 10's to 100's of kilometres apart, thus features lying between are not visible to the system. Alternatively multibeam echo sounders emit a fan of sound beams to the seafloor to scan a wide swath of the seabed in great detail and thus mapping all features on the seabed.
Multibeam echo sounder system
Hull-mounted on the RV Tangaroa, the EM-302 multibeam echosounder maps the seafloor using a fan of 288 acoustic beams, producing up to 864 soundings per ping in dual swath mode, providing 100% coverage of the seabed. Only recently have oceanographers been able to map the seabed in something near the detail possible on land. Using acoustic technology we can now produce accurate, aerial-like images of the seafloor. See Figure 5.
Discovering the ocean floor
In 1874, HMS Challenger conducted the first oceanographic survey of the world ocean. This was the start of systematic charting of the southwest Pacific Ocean. Since then, successive surveys by naval and oceanographic ships have greatly improved our knowledge of the 4 million square kilometres of ocean enclosed by the New Zealand Exclusive Economic Zone. See Figure 6.
View and purchase printed copies of our charts and posters
Map information and metadata
Projection Mercator (WGS84 Datum) at 41°S.
This chart includes all of British Admiralty areas 383, 384, 385, 414, 415, 416, 445, 446, 447, 474, 475, 476, 501 and parts of 382, 386, 500, 524, 525, 526.
Digital data information
Projection Mercator (WGS84 Datum) at 41°S true latitude and 100°E central meridian (EPSG 3994).
Bibliographic reference
CANZ, 2008: New Zealand Region Bathymetry, 1:4 000 000, 2nd Edition. NIWA Chart, Miscellaneous Series No. 85.
Attribution: Content, Datasets and Imagery provided by NIWA
Source information - Hauraki Gulf bathymetry
Onshore land representation derived from Land Information New Zealand topographic and the Ministry for the Environment LCDB II digital datasets.
Offshore representation derived from Land Information New Zealand hydrographic and NIWA bathymetric surveys.
Not to be used for navigational purposes.
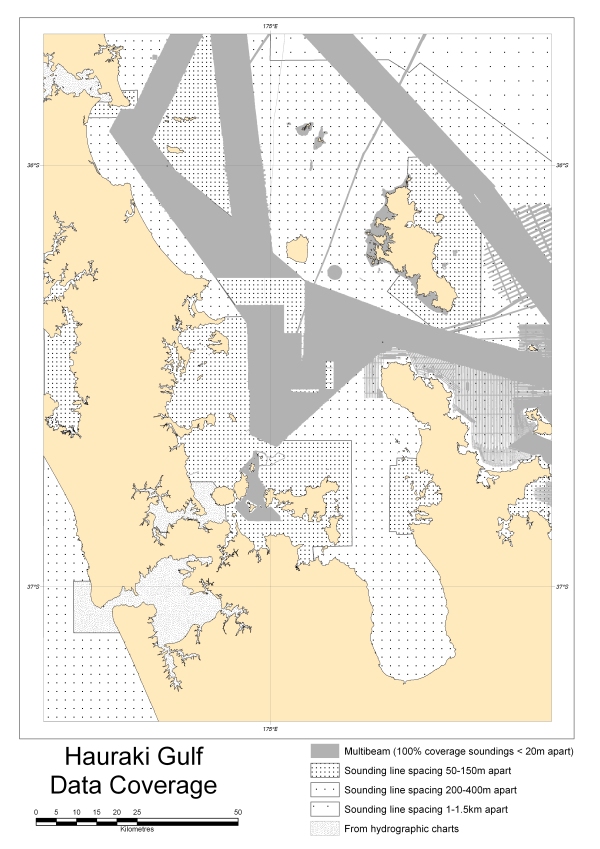
Hauraki Gulf data coverage
Denotes areas where multibeam swath and single beam information of the Hauraki seafloor have been acquired. Data confidence is greater in areas of dense coverage (gray) versus areas of sparse coverage (white). See Figure 7.
Map information and metadata
Projection Mercator (WGS84 Datum) at 41°S.
Digital data information
Projection Mercator (WGS84 Datum) at 41°S true latitude and 100°E central meridian (EPSG 3994).
Bibliographic reference
Mackay, K.A., Mackay, E.J., Neil, H.L., Mitchell, J.S., Bardsley, S.A., 2012: Hauraki Gulf. NIWA Chart, Miscellaneous Series 91
Published by the National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research Ltd
Copyright © All rights reserved
Attribution: Content, Datasets and Imagery compiled by NIWA, from data sourced from NIWA and LINZ.