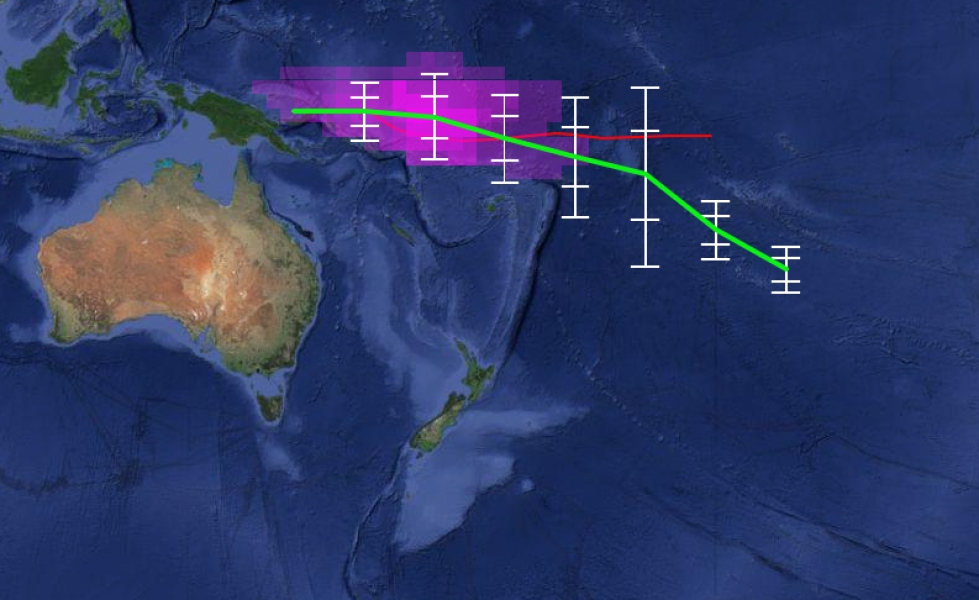
The ensemble of global climate models for rainfall that are used in METPI show an area of higher than normal rainfall associated with the SPCZ position.
The green line indicates the average SPCZ position for the forecast period based on the average of eight climate models.
The white vertical bars and ‘whiskers’ indicate the one and two standard deviations between the model projections of the SPCZ position every five degrees of longitude.
The purple shading is proportional to the probability of intense convection developing within the SPCZ.
During the May to July 2015 period, the South Pacific Convergence Zone (SPCZ) is expected to be north of normal to the west of the International Dateline. This region of the SPCZ is also expected to experience higher than normal convection and rainfall during the forecast period. Confidence about the SPCZ position is reduced to the east of the International Dateline.