A regional climatology is a summary of the typical weather and climate of a region, based on historical data observations made at climate stations located within the region.
-
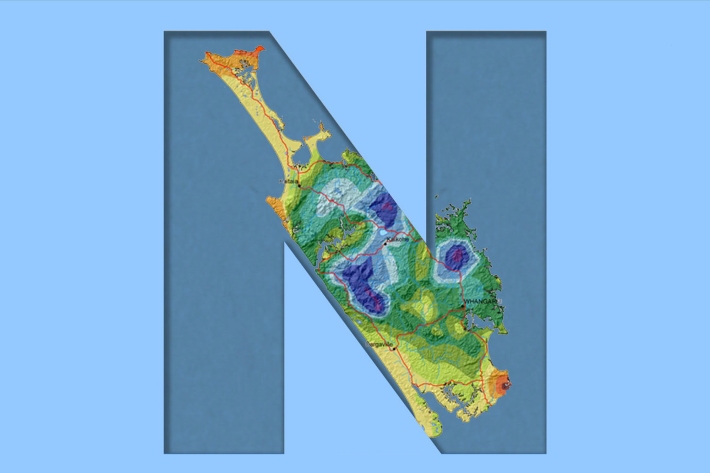
Northland
Northland, with its northern location, low elevation and close proximity to the sea is characterised by a mild, humid, and rather windy climate. -
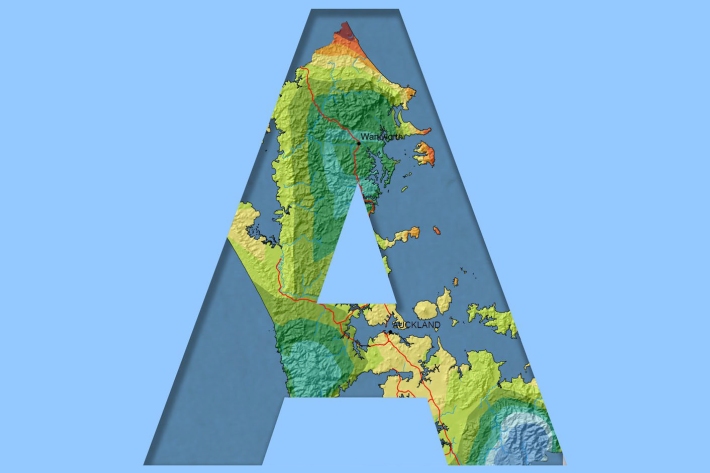
Auckland
Auckland experiences a subtropical climate. The region lies some 13° of latitude south of the Tropic of Capricorn, so tropical plants which are protected for the winter months will flower and fruit in the summer. -

Bay of Plenty
The topography of the North Island has a profound effect on the weather of the Bay of Plenty region. -
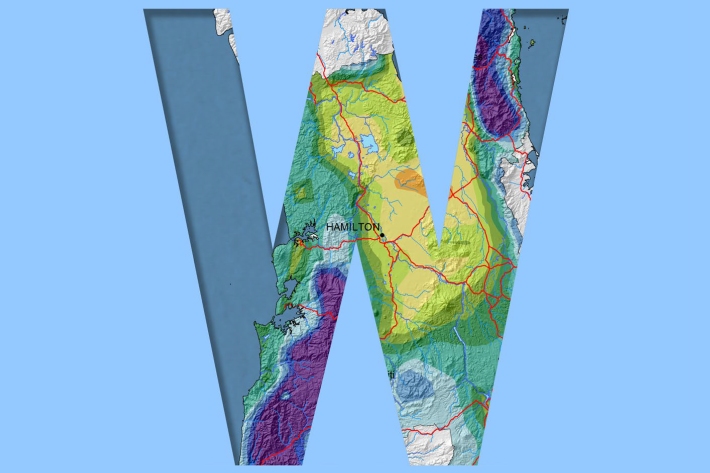
Waikato
Waikato exhibits a range of climates due to the variety of landscapes in the region. -

Gisborne
In comparison with regions exposed to the west, Gisborne experiences a greater number of weather and climatic extremes. -
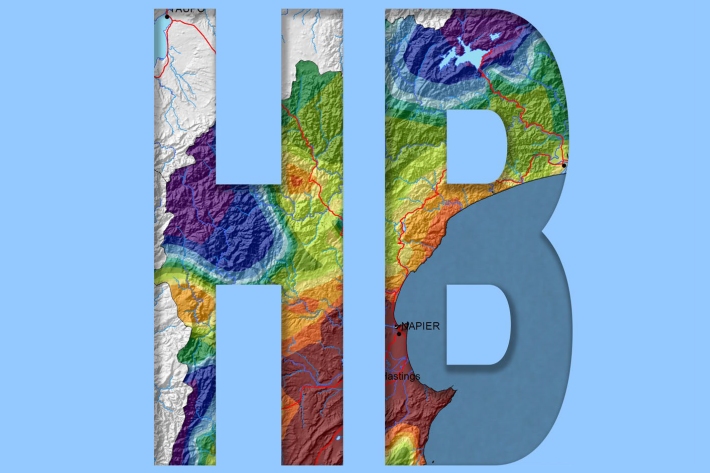
Hawkes Bay
The climate of Hawke’s Bay is influenced largely by the orography and the airstreams crossing New Zealand. -
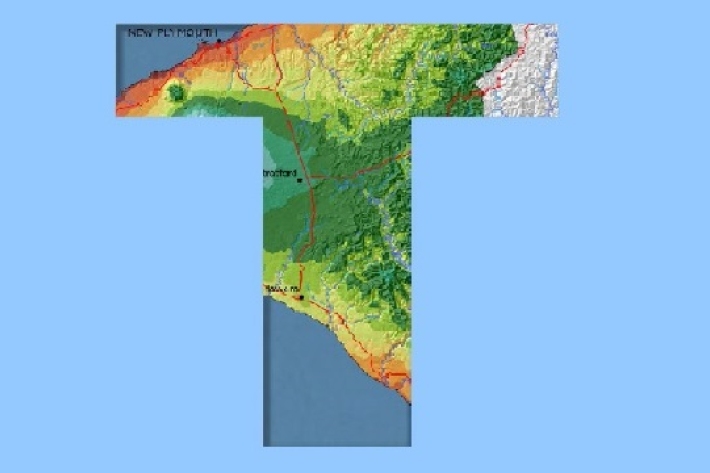
Taranaki
The climate of Taranaki is determined largely by its position in relation to the large scale weather patterns affecting New Zealand. -
Manawatu-Wanganui
The climate of the Manawatu-Wanganui region is a reflection of the generally disturbed westerly air flow with interspersed anticyclones, modified in specific places by the local topography. -
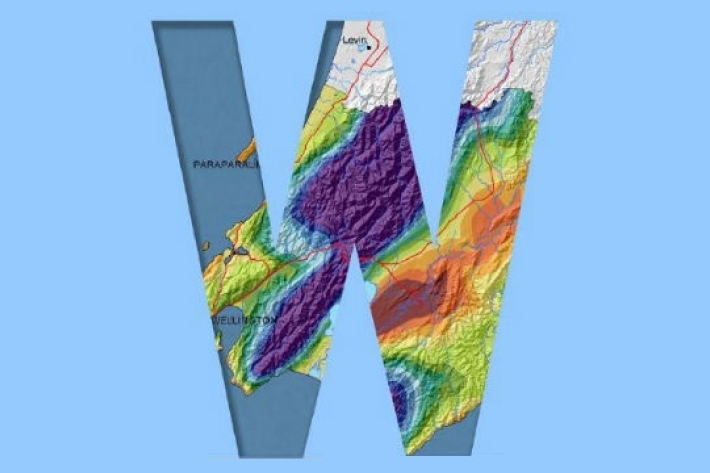
Wellington
The climate and weather of the Wellington region is characterised by strong variations in space and time, strongly influenced by the presence of Cook Straight and the rugged local topography. -
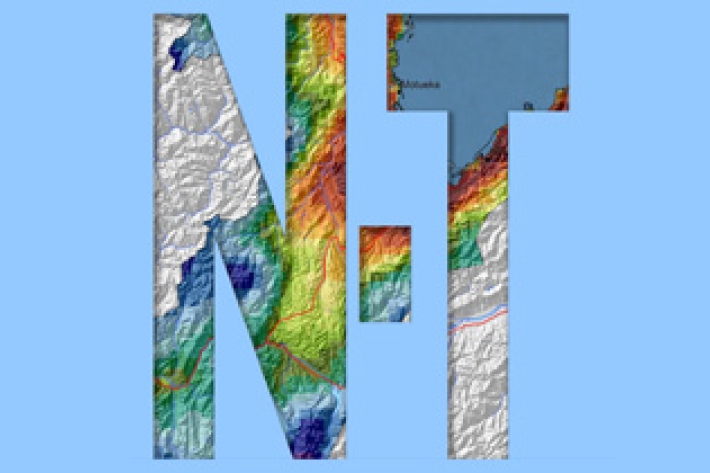
Nelson and Tasman
Nelson City and Tasman District are located in the most north-westerly part of the South Island and generally are the first to be influenced by weather systems moving onto the island from the north. -
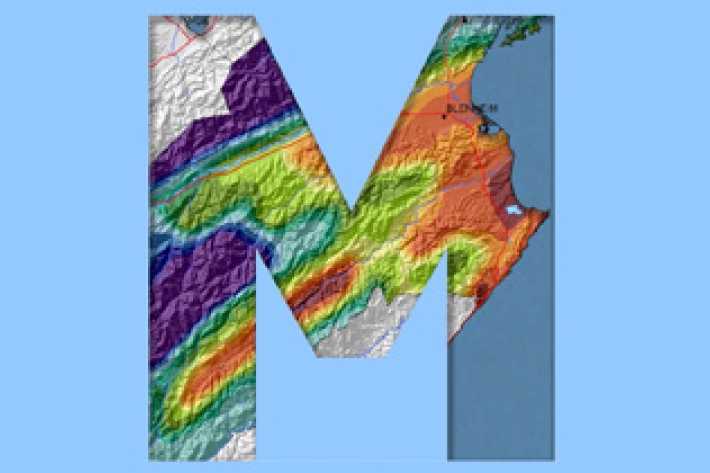
Marlborough
The main characteristic of the Marlborough climate is its dryness. Summer droughts are frequent, and the region is often swept by warm, dry northwesterlies. -
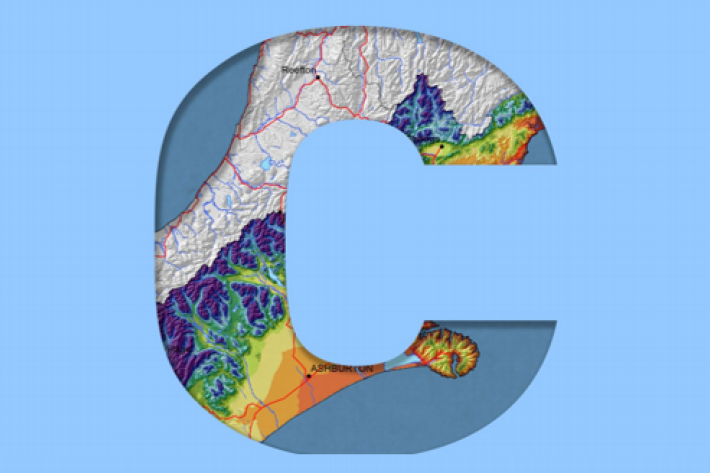
Canterbury
All aspects of the climate of Canterbury are dominated by the influence of the Southern Alps on the prevailing westerly airflows. -
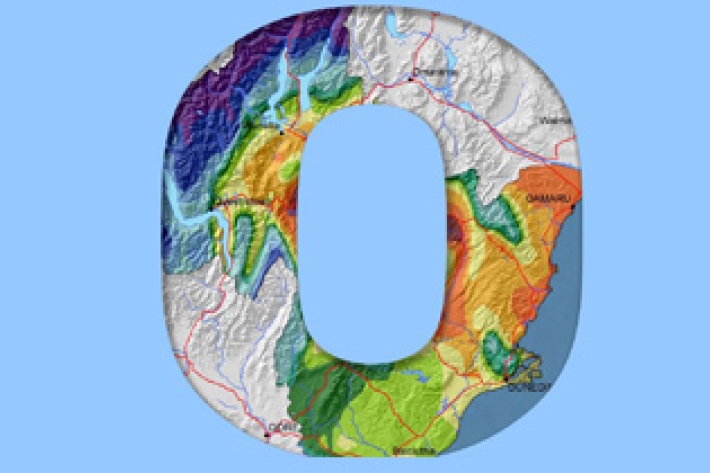
Otago
The climate of Otago is perhaps the most diverse of any region in New Zealand. -
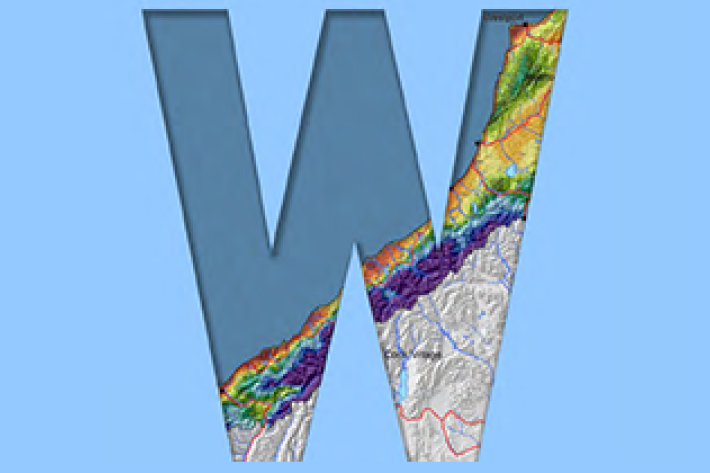

West Coast
West Coast is New Zealand’s wettest region, and this may be attributed to its exposure to the predominant westerly airflow over the country, combined with the orographic effect of the Southern Alps. -
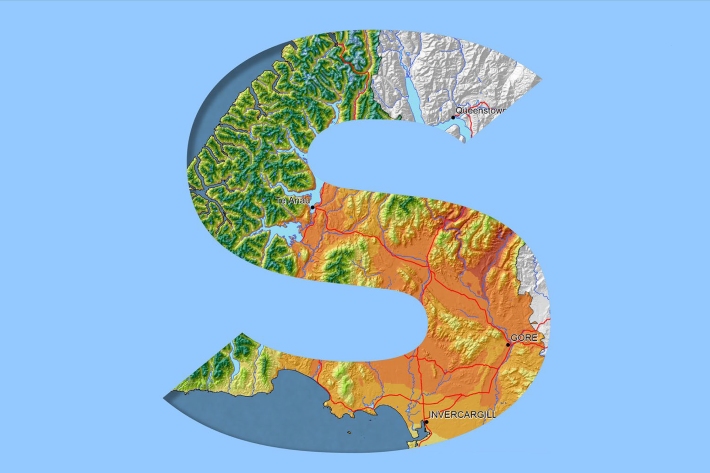
Southland
Southland is both the most southerly and most westerly part of New Zealand and generally is the first to be influenced by weather systems moving onto the country from the west or south. -

Chatham Islands
The weather of the Chatham Islands is marked by rapid changes of conditions, and typically windy cloudy conditions. -
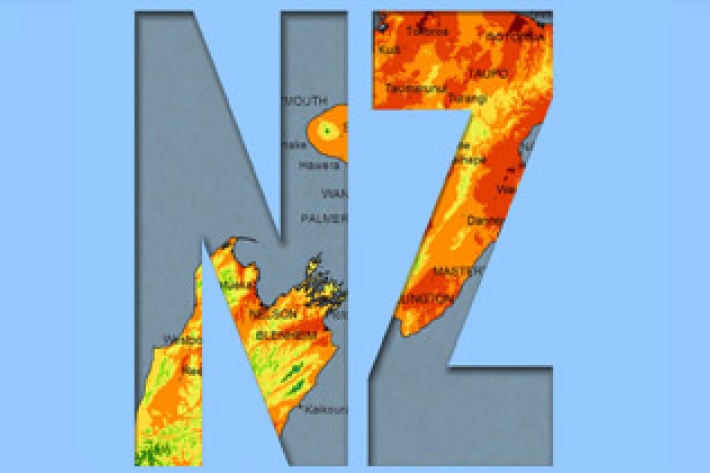

New Zealand
New Zealand is situated in the latitudes of prevailing westerlies and exposed coastal locations often experience strong winds, with generally lighter winds elsewhere.